Introduction
Polyurethane foam is a multipurpose substance that is utilised in many different industries, from packaging and insulation to furniture and car seats. While the natural appearance of polyurethane foam is typically off-white or yellowish, the demand for colored polyurethane foams has increased significantly. Colored foams open up new possibilities for design, branding, and functionality. But have you ever wondered what goes into making polyurethane foam colored? This article delves into the science behind colored polyurethane foams, focusing on their formulation, pigmentation techniques, and challenges involved in achieving vibrant, durable colors.
Definition
Colored polyurethane foams are versatile, lightweight materials made by incorporating pigments or dyes into polyurethane foam during the manufacturing process. These foams combine the inherent cushioning, insulation, and durability properties of polyurethane with vibrant or customized colors, making them ideal for applications in upholstery, packaging, automotive interiors, and decorative products where both function and aesthetic appeal are important.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
A polymer made of organic units connected by carbamate (urethane) bonds is called polyurethane foam. It is created through a chemical reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, catalyzed by various additives. Depending on the formulation and process, polyurethane foam can be either flexible or rigid, each serving different applications:
- Flexible polyurethane foam is frequently found in car seats, cushions, and beds.
- Rigid polyurethane foam is used for refrigeration and construction insulation.
Foams are cellular structures filled with air pockets, giving them light weight and cushioning properties.
Why Color Polyurethane Foam?
Coloring polyurethane foam offers several advantages:
Aesthetic Appeal: Colored foam enhances product appearance, allowing manufacturers to match specific color schemes or branding.
Functional Identification: Different colors can be used to denote varying foam grades or densities in manufacturing.
Customization: It offers product differentiation and customization options for consumers.
Improved User Experience: Color can affect user perception and comfort; for example, dark-colored foam may conceal stains better than white foam.
However, pigmentation is not as simple as mixing paint with foam—polyurethane chemistry demands precise methods and careful material selection to ensure color consistency and performance.
Fundamentals of Polyurethane Foam Formulation
Before discussing pigmentation, it’s important to understand the basic components involved in foam formulation:
- Polyols: These serve as the foam’s structural core and are usually polyester or polyether polyols.
- Isocyanates: React with polyols to form the polymer network.
- Blowing Agents: Substances that produce gas while the cellular structure is formed.
- Catalysts: Speed up the chemical reactions.
- Surfactants: Control foam cell size and stability.
- Additives: Flame retardants, stabilizers, and pigments.
The formulation is a delicate balance of these components, influencing foam properties like density, resilience, hardness, and durability.
Approaches to Coloring Polyurethane Foam
1. Pre-Reaction Pigmentation
This technique involves directly adding pigments or dyes to the polyol component before to the foam reaction starts. This approach ensures uniform dispersion of color throughout the foam.
- Pigments vs. Dyes: While dyes are soluble and dispersed molecularly, pigments are solid particles suspended in a medium. Pigments offer better lightfastness and chemical resistance, while dyes provide brighter colors but can fade faster.
- Challenges: Pigments must be finely milled to avoid clogging and maintain foam cell integrity. Pigment selection must consider compatibility with polyol chemistry to prevent reactions that affect foam quality.
- Dispersion: Proper dispersion using high-shear mixers or ultrasonic homogenizers is critical to avoid color streaking and pigment agglomerates.
2. Post-Reaction Coloring
This involves dyeing or coating the surface of the foam after it has been produced.
- Advantages: Easier to implement in some cases without modifying the foam formulation.
- Disadvantages: Color may not penetrate deeply, leading to uneven color under stress or cutting. Surface coatings may wear off with use.
3. Using Color Masterbatches
Masterbatches are concentrated mixtures of pigments in a carrier resin. They can be blended with polyols or added during foam processing.
- Benefits: Consistent color and easier handling compared to powders.
- Considerations: The carrier resin must be compatible with foam chemistry to avoid defects.
Types of Pigments Used in Polyurethane Foam
Selecting the right pigment is crucial for achieving vibrant, stable colors. Pigments fall into several categories:
- Organic Pigments: Provide bright colors like reds, blues, and yellows. They are less opaque but more prone to fading under UV exposure.
- Inorganic Pigments: Examples include titanium dioxide (white), iron oxides (reds, yellows, browns), and carbon black. They offer excellent durability and opacity.
- Specialty Pigments: Metallic, pearlescent, and fluorescent pigments add unique effects but are less common due to cost and processing complexity.
Challenges in Coloring Polyurethane Foam
Coloring polyurethane foam is technically challenging due to several factors:
Chemical Compatibility:
Pigments and dyes must be chemically inert with foam components. Some pigments can catalyze unwanted side reactions, affecting foam rise, curing time, or mechanical properties.
Foam Cell Structure:
Pigments can interfere with foam cell formation. Large pigment particles may disrupt the foam matrix, causing irregular cells, decreased resilience, or structural weaknesses.
Color Uniformity:
Achieving consistent color throughout a large foam block or batch requires meticulous pigment dispersion. Color streaks or blotches are unacceptable in commercial products.
UV and Heat Stability:
Foam products exposed to sunlight or heat can suffer pigment fading or discoloration. UV stabilizers and heat-resistant pigments are essential for outdoor or automotive applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations:
Some pigments contain heavy metals or toxic substances. Industry trends towards safer, environmentally friendly pigments are driven by regulatory compliance and environmental safety.
Innovations and Trends in Colored Polyurethane Foam
Recent advances in pigment technology and polyurethane chemistry have led to improvements:
- Nano-pigments: Nanoparticles provide better dispersion and color intensity without compromising foam structure.
- Biobased Pigments: Derived from natural sources, these offer sustainability benefits.
- Multi-Functional Pigments: Combining coloration with UV protection, antimicrobial properties, or flame retardancy.
- Digital Color Matching: Advanced software and spectrophotometry ensure precise color matching to brand standards.
Practical Applications of Colored Polyurethane Foam
- Furniture and Bedding: Custom colored foam for mattresses, cushions, and upholstered furniture.
- Automotive Industry: Colored foams used in car interiors for aesthetic and functional reasons.
- Packaging: Color-coded foam inserts to protect and identify fragile products.
- Footwear: Coloured foams for the insoles and midsoles to add uniqueness to the design.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, sports equipment, and household items benefit from vibrant foam colors.
Growth Rate of Colored Polyurethane Foams Market
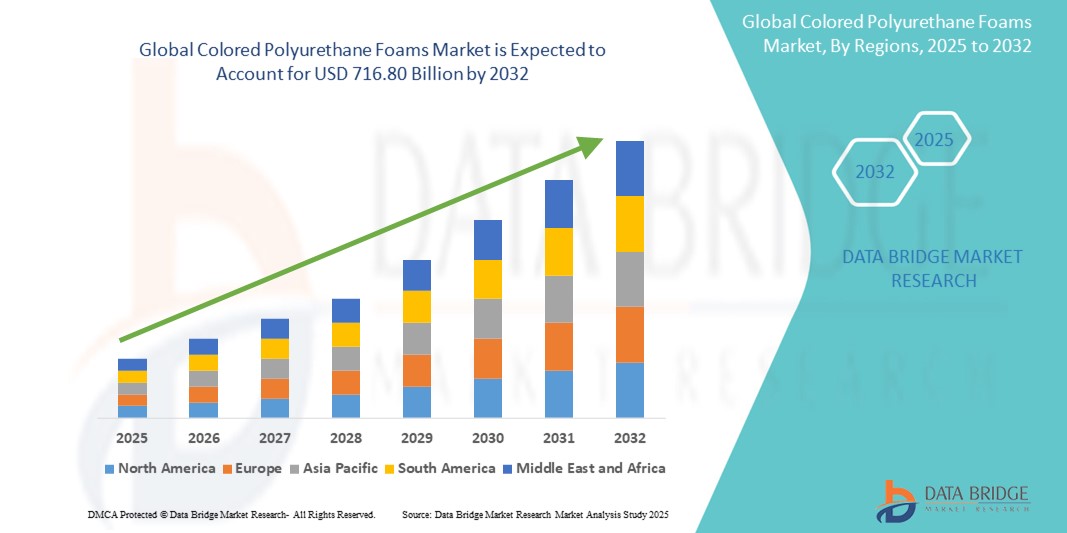
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the colored polyurethane foams market was estimated to be worth USD 36.28 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 45.2% to reach USD 716.80 billion by 2032.
For more insights on the autoimmune disease treatment Market visit:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-colored-polyurethane-foams-market
Conclusion
Colored polyurethane foams combine the material’s intrinsic versatility with the creative possibilities of color. Achieving high-quality colored foam requires deep understanding of polyurethane chemistry, pigment properties, and manufacturing processes. The careful selection and dispersion of pigments, attention to chemical compatibility, and consideration of environmental factors are all critical to success.