Introduction
In a world grappling with climate change, soil degradation, and increasing demands for sustainable agricultural practices, biochar is emerging as a powerful solution with multifaceted benefits. Biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from the pyrolysis of organic biomass, is being increasingly recognized for its ability to improve soil health, sequester carbon, and manage waste. As industries, governments, and farmers search for greener alternatives to traditional farming and waste disposal methods, the biochar market is witnessing a surge in global interest and investment.
This article explores the dynamics of the biochar market, including its production technologies, key application areas, regional trends, and future growth opportunities.
Understanding Biochar
Biochar is produced through a thermal decomposition process called pyrolysis, which involves heating organic material like wood chips, crop residues, or manure in an oxygen-limited environment. The result is a highly porous, stable form of carbon that can remain in the soil for hundreds to thousands of years.
Its porous nature allows biochar to retain water, nutrients, and beneficial microbes, making it an ideal soil amendment. Furthermore, since the process locks carbon from biomass into a stable form rather than releasing it as CO₂ or methane, biochar production contributes to carbon sequestration, a critical strategy in mitigating climate change.
Key Drivers of the Biochar Market
1. Sustainable Agriculture Demand
The agricultural industry is under pressure to improve yields while reducing its environmental footprint. Biochar has proven benefits in enhancing soil fertility, reducing irrigation needs, and lowering dependency on chemical fertilizers. These advantages make it a compelling addition to modern sustainable farming practices.
2. Carbon Sequestration Initiatives
Governments and private organizations are actively promoting carbon-negative technologies. Biochar’s ability to trap atmospheric carbon and store it in soil aligns with global carbon reduction goals. This has led to increasing support through carbon credit markets and government incentives.
3. Waste Management Solutions
With the growing need for effective waste management strategies, biochar production provides a sustainable method for converting organic waste into a valuable product. Municipal waste, agricultural residues, and forestry byproducts can all be repurposed into biochar, reducing landfill burdens and emissions.
4. Water and Soil Conservation
Biochar enhances water retention in soil, which is particularly beneficial in arid and drought-prone regions. It also improves nutrient retention, reduces leaching, and supports microbial activity, contributing to healthier and more resilient ecosystems.
Key Applications of Biochar
1. Agriculture
Agriculture remains the largest application sector for biochar. Farmers use it to improve soil structure, pH balance, nutrient availability, and moisture retention. It is especially useful in degraded soils where traditional methods fall short.
2. Animal Husbandry
Biochar is increasingly being used as a feed additive to improve digestion in livestock and reduce methane emissions. It also finds use in bedding material for odor control and moisture management in barns.
3. Water Treatment
Thanks to its high porosity and surface area, biochar can filter heavy metals and organic pollutants from water. It is gaining popularity as a low-cost alternative for rural and industrial wastewater treatment.
4. Construction Materials
Biochar-infused concrete and insulation materials are being explored for sustainable building practices. These products not only reduce emissions but also contribute to carbon storage within building materials.
5. Energy Production
Some advanced applications include the use of biochar in energy storage devices and as a replacement for coal in power plants, especially where biochar’s carbon neutrality is a key advantage.
Market Segmentation Overview
The biochar market can be segmented based on technology, feedstock, application, and region:
- Technology: Slow pyrolysis, fast pyrolysis, gasification, and hydrothermal carbonization.
- Feedstock: Agricultural residues, forestry waste, animal manure, and others.
- Application: Agriculture, livestock farming, water treatment, construction, and energy.
- Region: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Among these, slow pyrolysis is the most widely used method due to its efficiency in producing high-quality biochar with minimal emissions.
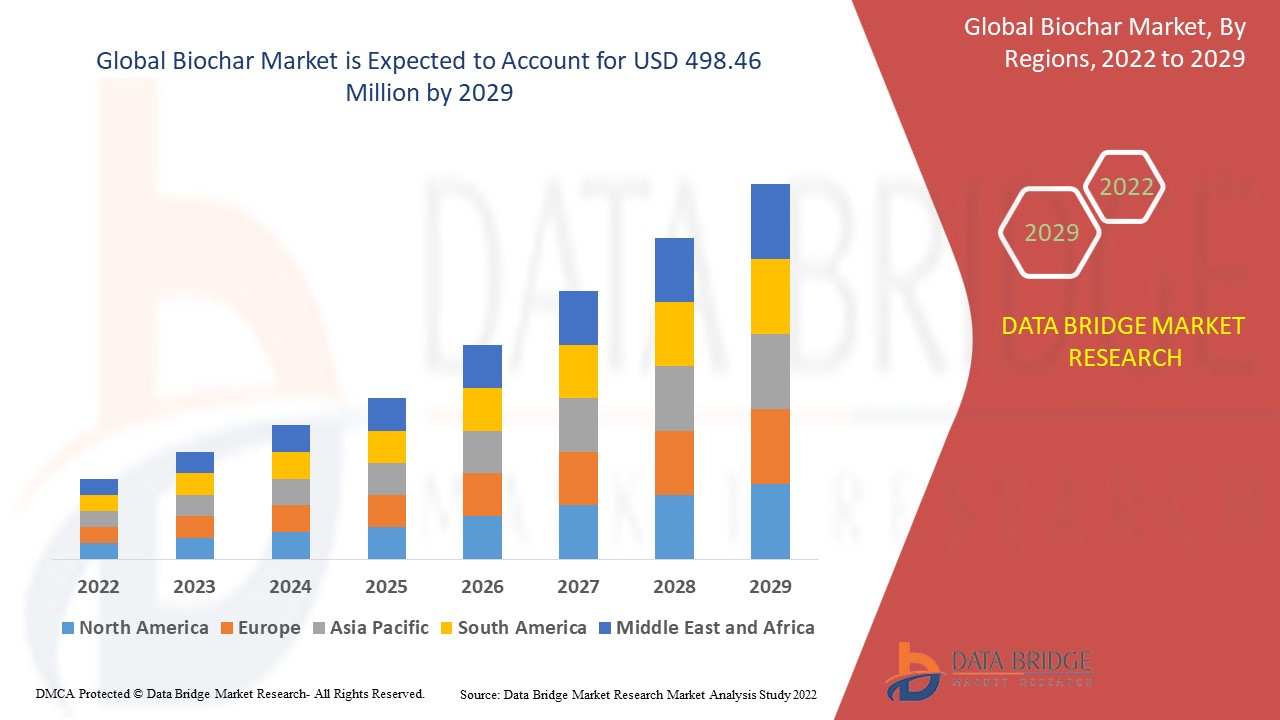
Regional Market Insights
North America
North America dominates the global biochar market owing to strong governmental support, well-established farming practices, and an increasing focus on carbon credits. The U.S. leads in terms of production and consumption.
Europe
Europe is witnessing significant growth, driven by the EU’s climate targets and sustainable agriculture mandates. Countries like Germany, the UK, and the Netherlands are investing in biochar research and commercialization.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific presents immense potential due to large agricultural sectors in countries like China and India. The region is also addressing challenges like soil degradation and air pollution, for which biochar offers practical solutions.
Latin America and MEA
These regions are slowly gaining momentum, particularly in agricultural use. With support from international environmental organizations and growing awareness, market penetration is expected to rise.
Market Challenges
Despite its promising outlook, the biochar market faces several challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Setting up pyrolysis plants involves substantial capital costs, which can be a barrier for small-scale producers and farmers.
- Lack of Standardization: The absence of uniform quality standards across countries and sectors makes it difficult for producers to scale operations and enter new markets.
- Limited Awareness: Many potential users, particularly in developing countries, are still unaware of biochar’s benefits and applications.
- Regulatory Barriers: In some regions, unclear regulations around biochar classification (as a fertilizer, waste product, or carbon sink) hinder market expansion.
Future Outlook and Opportunities
The future of the biochar market looks robust, driven by a combination of environmental urgency and technological advancement. Some promising trends include:
- Carbon Credit Integration: Monetizing the carbon sequestration potential of biochar through verified carbon credits is likely to attract more investment.
- Product Innovation: Innovations in blended biochar products tailored for specific soil types and crops are expanding its appeal in agriculture.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between governments, research institutions, and private players are accelerating large-scale adoption.
- Circular Economy Models: As part of broader zero-waste initiatives, industries are incorporating biochar into their sustainability strategies.
With growing emphasis on regenerative agriculture, climate-smart practices, and eco-friendly materials, biochar is set to play a transformative role in shaping the global sustainability landscape.
Conclusion
The biochar market stands at a crossroads where environmental necessity meets economic opportunity. As a versatile and sustainable solution, biochar addresses multiple global challenges—from improving soil and water health to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and managing organic waste. With technological innovation, policy support, and greater awareness, biochar is poised to transition from a niche product to a mainstream environmental and agricultural tool.
Read More : https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-biochar-market