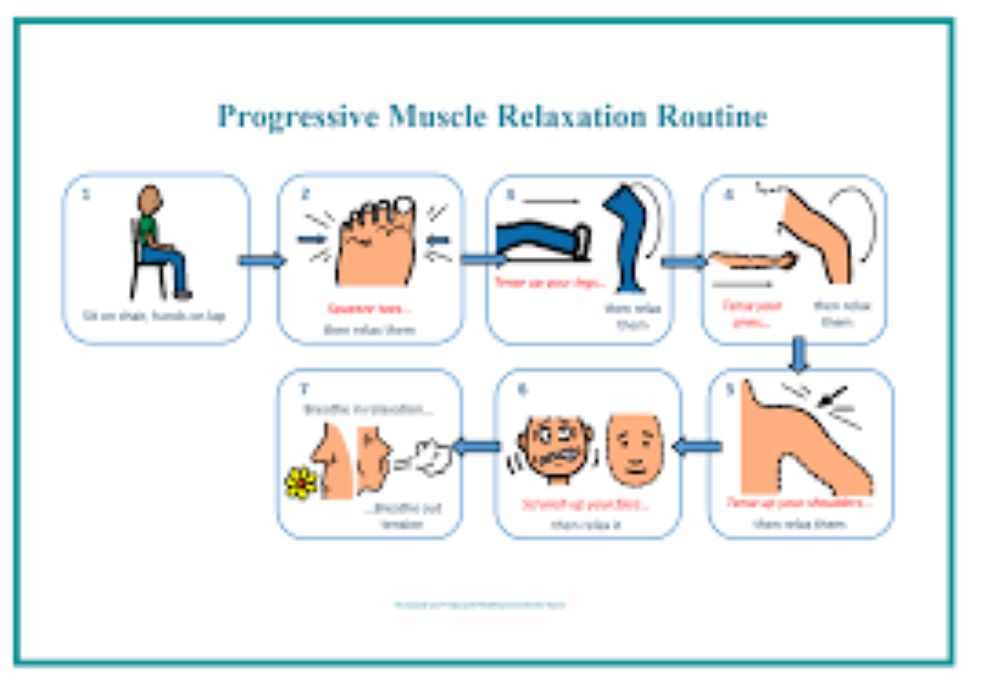
Anxiety and stress are common problems many people face. They can affect your daily life, making it hard to focus, sleep, or enjoy activities. One way to manage these feelings is by using muscle relaxants. These medications help reduce tension in the body, which can calm the mind. This article explains how muscle relaxants work, their benefits, and things to consider before using them.
What Are Muscle Relaxants?
Muscle relaxants are medications that help reduce muscle tension and spasms. They work by targeting the nervous system, which controls muscle movement. When muscles are tense, it can lead to pain and discomfort. Muscle relaxants ease this tension, helping the body feel more relaxed.
There are two main types of muscle relaxants: antispasmodics and neuromuscular blockers. Antispasmodics are commonly used for anxiety and stress because they directly reduce muscle tightness. Neuromuscular blockers are typically used during surgeries to prevent muscle movement.
How Muscle Relaxants Help with Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress often cause physical symptoms. These include muscle tightness, headaches, and a racing heart. When your body feels tense, it can make your mind feel the same way. Antispasmodics break this cycle by calming the body.
By reducing muscle tension, these medications help you feel more at ease. This physical relaxation can lead to mental relaxation. When your body is not tense, your mind can focus better, and you may feel less overwhelmed.
Benefits of Using Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants offer several benefits for people dealing with anxiety and stress:
- Reduce Physical Tension: They ease tight muscles, which can relieve pain and discomfort.
- Improve Sleep: Relaxed muscles make it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Enhance Mood: When your body feels calm, your mind often follows, leading to a better mood.
- Increase Focus: Reduced tension helps you concentrate on tasks without distractions.
Common Muscle Relaxants for Anxiety and Stress
Several muscle relaxants are commonly used to manage anxiety and stress. These include:
- Benzodiazepines: Medications like Valium and Xanax are often prescribed for anxiety. They relax muscles and calm the mind.
- Cyclobenzaprine: This medication is used for short-term relief of muscle spasms and tension.
- Baclofen: It helps reduce muscle stiffness and is often used for chronic conditions.
- Methocarbamol: This relaxant is used to treat muscle pain and spasms caused by stress or injury.
Always consult a doctor before using any medication. They can recommend the best option for your needs.
How to Use Muscle Relaxants Safely
Using antispasmodics requires caution. These medications can cause side effects like drowsiness, dizziness, and dependency. Follow these tips to use them safely:
- Follow Doctor’s Instructions: Take the prescribed dose and do not exceed it.
- Avoid Alcohol: Mixing spasmolytics with alcohol can increase side effects.
- Do Not Drive: These medications can make you drowsy, so avoid driving or operating machinery.
- Monitor Side Effects: If you experience severe side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Natural Alternatives to Muscle Relaxants
If you prefer not to use medication, there are natural ways to relax your muscles and reduce anxiety:
- Exercise: Physical activity releases endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress.
- Yoga: Stretching and breathing exercises in yoga help relax muscles and calm the mind.
- Meditation: Mindfulness practices can reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
- Warm Baths: Soaking in warm water eases muscle tension and helps you unwind.
Risks and Side Effects of Muscle Relaxants
While Neuromuscular blockers can be helpful, they come with risks. Common side effects include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
In some cases, these medications can lead to dependency or addiction. Long-term use is not recommended. Always discuss the risks with your doctor before starting any medication.
Who Should Avoid Muscle Relaxants?
Skeletal Neuromuscular blockers are not suitable for everyone. Certain groups should avoid them or use them with caution:
- Pregnant Women: These medications can affect the baby.
- Elderly Individuals: Older adults are more sensitive to side effects like drowsiness.
- People with Liver or Kidney Problems: These organs process medications, so impaired function can increase risks.
- Those with a History of Substance Abuse: Muscle relaxants can be addictive for some people.
Combining Muscle Relaxants with Other Treatments
Muscle relaxants work best when combined with other treatments. Therapy, exercise, and lifestyle changes can enhance their effects. For example:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps address the root causes of anxiety.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity reduces stress and improves overall health.
- Healthy Diet: Eating nutritious foods supports mental and physical well-being.
When to See a Doctor
If anxiety and stress are affecting your daily life, it’s important to seek help. A doctor can assess your symptoms and recommend the best treatment plan. They may suggest Muscle depressants, therapy, or other options.
Do not self-medicate. Using Spasmolytics without a prescription can be dangerous. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
Conclusion
Antispasmodics can be an effective tool for managing anxiety and stress. They work by reducing muscle tension, which helps calm the mind. However, they come with risks and should be used carefully. Always consult a doctor before using these medications. Combining muscle relaxants with other treatments, like therapy and exercise, can provide the best results. If you’re struggling with anxiety and stress, don’t hesitate to seek professional help.